Myo and D-Chiro Inositol: Differences and Benefits

Originally published 09/11/2021. Updated for accuracy and relevancy on 11/09/2023
What is inositol, and why are there so many different names for it? Learn more about this naturally occurring carbohydrate, and why it may be helpful for women with PCOS.
By OBGYN and fertility expert Dr. Kenosha Gleaton
Did you know that metabolic syndrome, depression, diabetes, and PCOS are all tied to the same supplement? Inositol is a member of the vitamin B complex group and is found in foods such as fruits, beans, whole grains, and seeds, as well as in supplements. [1] Inositol impacts neurotransmitters in the body, has been shown to improve insulin function, and might even improve fertilization rates. [2-3]
What Is Inositol?
Inositol is a naturally occurring, vitamin-like carbohydrate that’s found in your body. It’s most abundant in the brain and tissues and has a large effect on hormones and other neurotransmitters. [1]
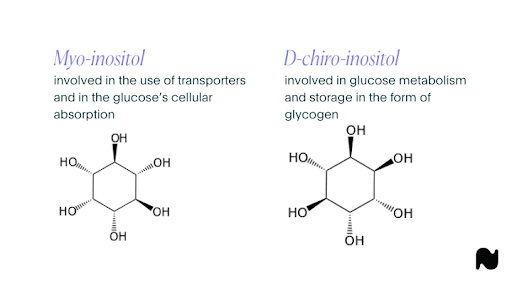
Inositol is frequently used for metabolic syndrome and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), as well as other medical and mental conditions. [3,4] There are many forms of inositol, but the two most common are myo-inositol (MI) and D-chiro-inositol (DCI).
Is Myo Inositol the Same As Inositol?
There are actually nine different types, or isomers, of inositol. [5] The main difference between isomers of inositol is in the function of the various compounds.
Generally, the term inositol is used to refer to the most bioavailable type, myo-inositol (MI). MI is often recommended for people with PCOS because many are often insulin resistant and myo-inositol may improve insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin levels.
What Is the Best Inositol Supplement?
There really isn’t a “best” form of inositol, just different functions. The real question you should be asking is how you want inositol to interact with your hormones, and what ratio will be most effective for you.
Difference Between Myo and D-Chiro Inositol
Myo-inositol (MI) and D-chiro inositol (DCI) both act as messengers in the body, but they carry out two different functions. [6] MI helps with the activation and use of substances and hormones, whereas DCI is involved in storage and synthesis. [6] Research shows that for most treatments, a mix of DCI and MI works most effectively. [7] In fact, every organ has a certain MI/DCI ratio related to its function.
Inositol Formula
Each organ has a specific MI/DCI ratio related to its function. In the ovary, MI enhances the action of FSH, via anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), and DCI is responsible for an excess production of insulin-dependent testosterone. [8] According to scientists, MI has been found in follicular fluid and appears to improve oocyte and embryo quality.
A study focused on PCOS found that when administered alone, DCI can have a negative impact on ovarian cell quality. [9] However, with a 40:1 ratio between MI/DCI administered together, plasma concentrations are mimicked and PCOS is counteracted at both systemic and ovarian levels. However, a Chochrane review warns there aren’t yet enough quality studies on this to prove inositol improves pregnancy rates or live birth for patients with PCOS. [10]
Key Takeaways
- Inositol may be useful for PCOS, IVF, and more.
- Inositol is a member of the vitamin B complex group and a naturally occurring carbohydrate.
- There are nine different isomers of inositol; they are mostly differentiated by their function in the body.
- A ratio of 40:1 of MI/DCI has been found to be the most effective formula for PCOS.
Up Next
- Which Inositol is best for people with PCOS?
- Can Inositol Increase Fertility?
- Getting pregnant with PCOS: Guide & treatment options
References:
- López-Gambero AJ, Sanjuan C, Serrano-Castro PJ, Suárez J, Rodríguez de Fonseca F. The Biomedical Uses of Inositols: A Nutraceutical Approach to Metabolic Dysfunction in Aging and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomedicines. 2020;8(9):295. Published 2020 Aug 20. doi:10.3390/biomedicines8090295
- Bevilacqua A, Bizzarri M. Inositols in Insulin Signaling and Glucose Metabolism. Int J Endocrinol. 2018;2018:1968450. Published 2018 Nov 25. doi:10.1155/2018/1968450
- Regidor PA, Schindler AE, Lesoine B, Druckman R. Management of women with PCOS using myo-inositol and folic acid. New clinical data and review of the literature. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2018;34(2):/j/hmbci.2018.34.issue-2/hmbci-2017-0067/hmbci-2017-0067.xml. Published 2018 Mar 2. doi:10.1515/hmbci-2017-0067
- Pintaudi B, Di Vieste G, Bonomo M. The Effectiveness of Myo-Inositol and D-Chiro Inositol Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes. Int J Endocrinol. 2016;2016:9132052. doi:10.1155/2016/9132052
- Potential role and therapeutic interests of myo-inositol in metabolic diseases - Scientific Figure on ResearchGate. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Structures-of-the-nine-stereoisomers-of-inositol-Inositol-exists-under-9-stereoisomeric_fig3_237839483 [accessed 9 Nov, 2023]
- THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INOSITOL, MYO-INOSITOL AND D-CHIRO INOSITOL. Inositoli. Accessed November 2023. https://www.inositoli.it/en/the-difference-between-inositol-myo-inositol-and-d-chiro-inositol/
- Nordio M, Proietti E. The combined therapy with myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol reduces the risk of metabolic disease in PCOS overweight patients compared to myo-inositol supplementation alone. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2012;16(5):575-581.
- Merviel, P., James, P., Bouée, S. et al. Impact of myo-inositol treatment in women with polycystic ovary syndrome in assisted reproductive technologies. Reprod Health 18, 13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-021-01073-3
- Dinicola S, Chiu TT, Unfer V, Carlomagno G, Bizzarri M. The rationale of the myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol combined treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome. J Clin Pharmacol. 2014;54(10):1079-1092. doi:10.1002/jcph.362
- Showell MG, Mackenzie-Proctor R, Jordan V, Hodgson R, Farquhar C. Inositol for subfertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;12(12):CD012378. Published 2018 Dec 20. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012378.pub2
Reach Out, We're Here
Have questions about your order or products? For the speediest answer, check out our FAQ section. Need something else? Come find us below.
Please keep in mind our regular business hours; Monday-Friday, 9am-5pm CT.
Customer Support
support@natalist.com
Press Inquiries
media@everlyhealth.com
Business & Partnerships
team@natalist.com
Affiliates + Influencers
team@natalist.com
Job Openings
Careers Page
























