An Overview of Nutrition Fact Acronyms and Abbreviations

Originally published 11/19/2020. Updated for accuracy and relevancy on 11/01/2023.
DV, DRI, RDI, RDA, AI, UL, oh my! There are a few important things to know when picking a supplement. This guide will walk you through them.
By Halle Tecco, MBA, MPH
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the way supplement manufacturers design nutrition facts labels, in order to standardize information across the industry. You may come across some acronyms when reading more about supplements, and we’re here to break it down for you!
Nutrition and Dietary Guidelines
The US government has provided nutrition advice to the public for over 100 years. This dietary guidance has generally included advice about what foods and nutrients to eat and drink for better health and has evolved over the years to reflect advances in nutrition science. [1]
In 1994, the US Congress passed the Dietary Supplement and Health Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994 to begin regulating the dietary supplement industry. [2] Since then, labeling has become an important aspect of supplements. The American National Standard helps confirm that what's on the label matches what's in the bottle. [3] In addition, testing is conducted to confirm that there are no unsafe levels of contaminants such as heavy metals, pesticides, and herbicides in the product. [3]
Supplement Bottle Labeling
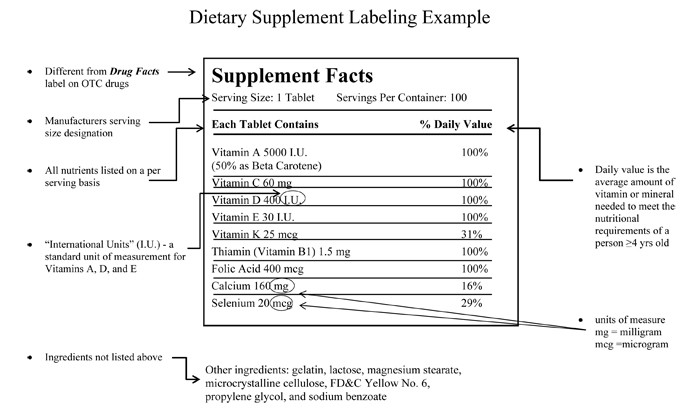
There’s a lot of information on the supplement facts portion of a supplement bottle. But what does it all mean? Here are a few things you’ll see on the supplement facts panel:
- Serving size is the manufacturer's suggested serving size. For example, a serving size could be “two tablets” or “four capsules.” Since consuming excessive levels of dietary supplements may have adverse health effects, be sure to follow the serving size instructions indicated on the label, or as instructed by your doctor.
- Servings per container is the quantity of pills/tablets/capsules divided by the serving size. So if a bottle of iron contains 90 tablets, and the serving size is three, then the number of servings per container is 30.
- International unit (IU) is a unit of measurement, frequently used for vitamins A and D. Defined individually for each substance, IUs are the quantity of a biologically active substance that produces a particular biological effect.
- MG and MCG are the abbreviations for milligram (mg) and microgram (mcg). MG is one thousandth of a gram, and mcg is one-millionth of a gram. These are common units of measurement for minerals and some vitamins, such as vitamin C.
- Daily value (DV) is the average amount of the vitamin or mineral needed to meet the nutritional requirements. More on this below.
Common Nutrition Fact Acronyms
- Daily Value (DV) is the recommended amount of nutrients to consume or not to exceed each day. They vary by sex and age and if you’re pregnant or breastfeeding. The NIH makes them available and is constantly updating the numbers as new research emerges.
- Percent Daily Value (%DV) is how much a nutrient in a single serving of an individual dietary supplement contributes to your daily diet. This is important because most nutrients can and should be consumed in a combination of diet and supplementation (if not diet alone). For example, if your prenatal has 50% DV for a particular nutrient, you will need to consume the other 50% via your diet. The FDA requires the actual amount and %DV of vitamin D, calcium, iron, and potassium be listed. While the other vitamins and minerals may be listed voluntarily by the manufacturer, we choose to be transparent with our customer, and therefore, list the full %DV in our Prenatal for her.
- Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) is the general term for a set of reference values used to plan and assess nutrient intakes of healthy people. These values, which vary by age and sex, include RDI, RDA, and UL. The Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine, National Academy of Sciences establishes principles and guidelines of adequate dietary intake and renders authoritative judgments on the relationships among food intake, nutrition, and health. [5]
- Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) is the average daily level of intake sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of nearly all healthy people (97-98%). The RDA for a nutrient is a value to be used as a goal for dietary intake by healthy individuals. The RDA is not intended to be used to assess the diets of either individuals or groups or to plan diets for groups.
- RDI (Reference Daily Intake) is a population-adjusted RDA based on all ages and sex groups of RDA values. It is numerically identical to the highest RDA value for any group. It was developed for food-labelling purposes.
- Estimated Average Requirement (EAR) is a value that helps set the RDA. The EAR is the daily intake value of a nutrient that is estimated to meet the nutrient requirement of half the healthy individuals in a particular life stage and sex.
- Adequate Intake (AI) is a value established when evidence is insufficient to develop an RDA. It is a value based on observed or experimentally determined approximations of nutrient intake by a group (or groups) of healthy people and is only used when an RDA cannot be determined.
- Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) is the largest daily intake of a nutrient considered safe for most people. Taking more than the UL is not recommended and may be harmful. For example, iron has a UL of 45 mg per day for adults over 19. [6] However, a doctor might prescribe more than the UL of iron to people who need higher doses in order to treat iron deficiency. For other nutrients, like B12, there is just not enough data to develop a UL or no data that shows adverse health effects at a maximum daily intake. [7] But just because a nutrient doesn’t have an established upper limit doesn’t mean you should take it in huge quantities. Always talk to your doctor about your supplement regimen.
So, there you have it! The FDA regulates the way supplement manufacturers design nutrition facts labels in order to standardize information across the industry, with the end goal of helping consumers knowledgeably compare products. Hopefully understanding these acronyms helps you make a more informed decision when shopping for supplements!
References:
- Dietary Guidelines for Americans. https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/
- Dietary Supplements. Office of Dietary Supplement Programs, HFS-810. Food and Drug Administration. 03/06/2023. https://www.fda.gov/food/dietary-supplements
- Dietary Supplements Claims, Labels and Regulations. National Sanitation Foundation. https://www.nsf.org/knowledge-library/dietary-supplements-claims-labels-regulations
- Consumer Healthcare Products Association. https://www.chpa.org/
- Nutrient Recommendations and Databases. NIH, Food and Nutrition Board of the National Academies of Sciences Engineering, and Medicine. https://ods.od.nih.gov/HealthInformation/Dietary_Reference_Intakes.aspx
- Iron. Fact Sheet for Consumers. NIH. August 17, 2023. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iron-Consumer/
- Vitamin B12. Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. NIH December 22, 2022. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-HealthProfessional/
Reach Out, We're Here
Have questions about your order or products? For the speediest answer, check out our FAQ section. Need something else? Come find us below.
Please keep in mind our regular business hours; Monday-Friday, 9am-5pm CT.
Customer Support
support@natalist.com
Press Inquiries
media@everlyhealth.com
Business & Partnerships
team@natalist.com
Affiliates + Influencers
team@natalist.com
Job Openings
Careers Page
























